Precision steel thread ring gauge for steel bar thread inspection
Description
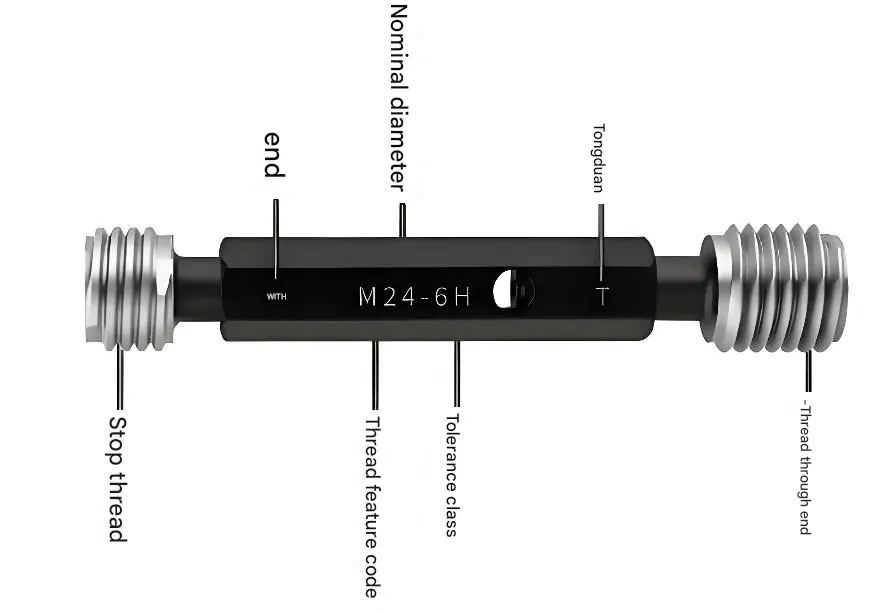
A thread ring gauge refers to the collective term for pass gauges (used to detect the upper limit of the mean diameter d2) and go gauges (used to detect the lower limit of the mean diameter d2) for inspecting external threads, as shown in the figure below.
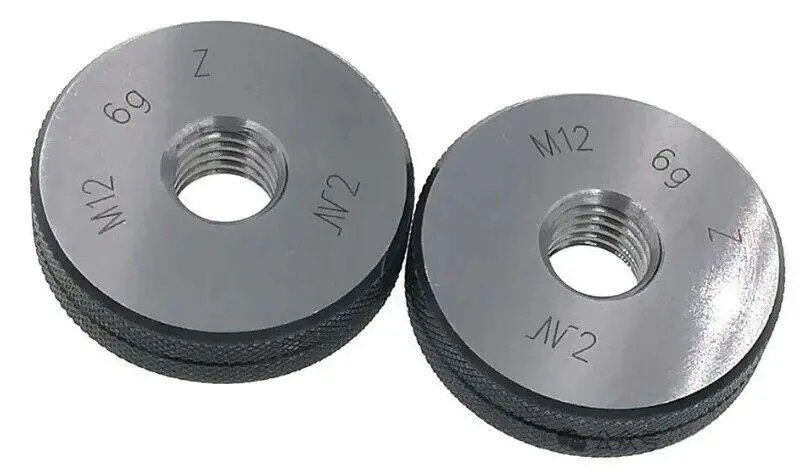

The Function of the Go Thread Ring Gauge and No-Go Thread Ring Gauge
Go Thread Ring Gauge:Used to detect the maximum physical dimensions of a part (i.e., the maximum allowable diameter of a shaft or the minimum allowable diameter of a hole). If the go gauge passes through the part smoothly, it indicates that the part dimensions have not exceeded the upper tolerance limit.
No-Go Thread Ring Gauge:Used to detect the minimum physical dimensions of a part (i.e., the minimum allowable diameter of a shaft or the maximum allowable diameter of a hole). If the plug gauge cannot pass through the part, it indicates that the part dimensions have not fallen below the lower tolerance limit.
Design Logic of Go Thread Ring Gauge and No-Go Thread Ring Gauge
1.Taylor’s Principle
The design of go gauges and no-go gauges follows Taylor’s principle, a core guideline proposed by British engineer William Taylor in 1905:
Go gauges should simulate the part’s “most severe fit condition”: for example, when inspecting a shaft, the go gauge’s shape must fully reflect the shaft’s maximum permissible dimension (including the impact of form errors);
A go gauge inspects only a single dimension: Typically designed with two-point contact (like a snap gauge) or a short cylindrical section (like a plug gauge), it verifies whether a local dimension exceeds tolerance.
This principle ensures that go/no-go gauges not only detect dimensional accuracy but also indirectly control the part’s form errors (such as roundness and straightness).
2、Go Gauge and No-Go Gauge
1、Inspection hole tool: Thread plug gauge
Go gauge: The pass end of the plug gauge simulates the insertion process of the mating component;
No-Go gauge: The stop end of the plug gauge only needs to check whether the local area around the hole opening is too large.
2、Tool for inspecting shafts: Thread ring gauge
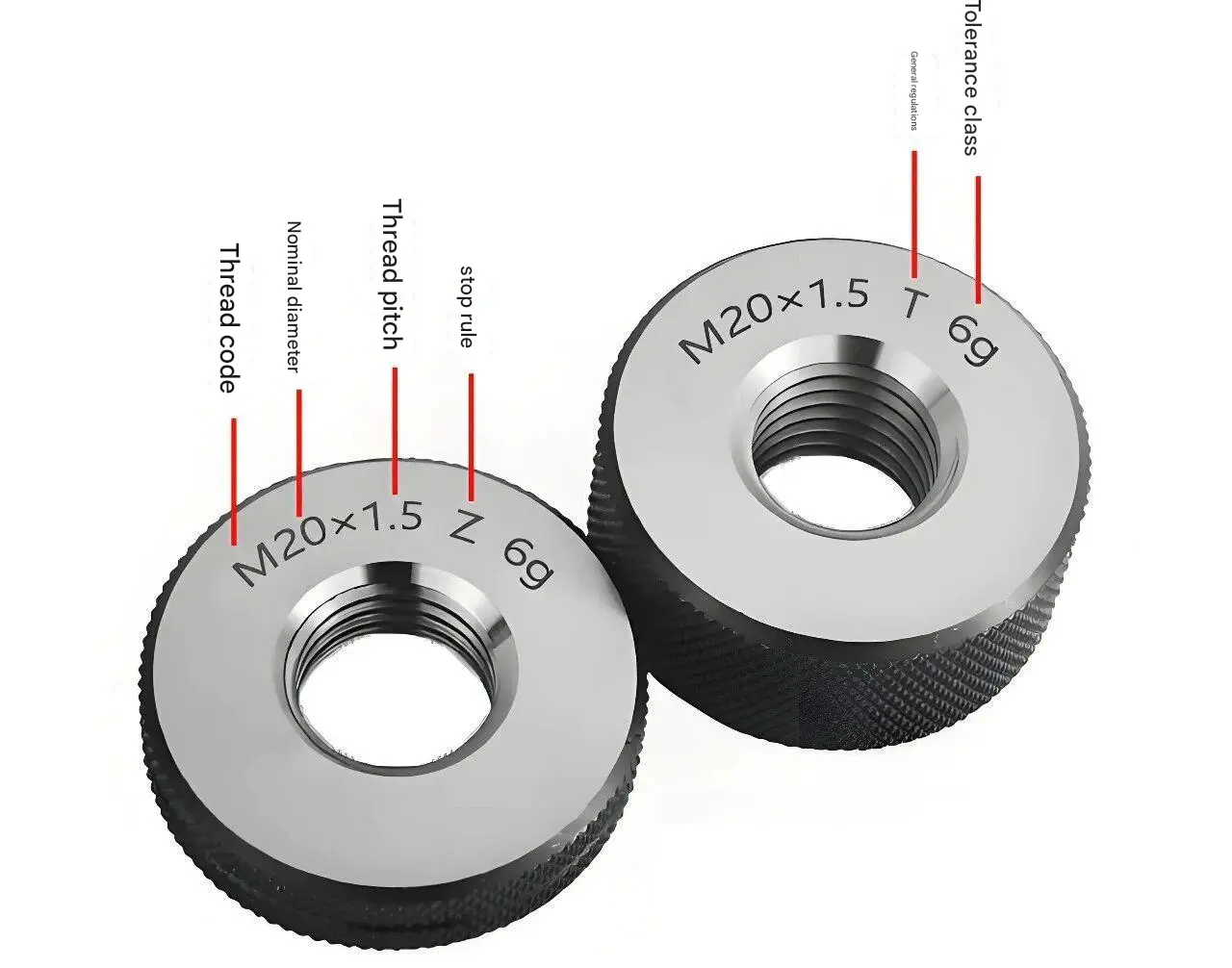

Go Gauge: Must fully encircle the shaft;
No-Go gauge: Only checks whether the shaft diameter is undersized.
Usage of Go Gauges and No-Go Gauges
Operating Procedure (Using the Test Hole as an Example)
1. Using a go thread ring gauge: Insert the go end vertically into the hole using only its own weight or light pressure (do not force it by striking). If the go end passes through the entire length of the hole naturally, the hole diameter is not less than the lower limit.
2. Using a no-go thread ring gauge: Attempt to insert the no-go end into the hole. If the no-go gauge cannot enter the hole opening by more than 1–2 mm (specific standards depend on industry regulations), the hole diameter has not exceeded the upper limit.
Example: For a hole marked “Φ10H7” (tolerance range Φ10.000~10.015mm): The go plug is designed with a diameter of 10.000mm (minimum hole size). If it passes through the hole, the hole is not smaller than the lower limit. The no-go plug is designed with a diameter of 10.015mm (maximum hole size). If it does not pass, the hole is not larger than the upper limit.
3. Comprehensive Judgment: If the go gauge passes and the no-go gauge stops, the hole diameter is acceptable; otherwise, it is unacceptable.
Precautions for Using Thread Ring Gauges
- The tolerance grade and deviation code of the workpiece’s thread must match the tolerance grade and deviation code marked on the plug gauge for proper use.
- Only when both the go gauge and no-go gauge are used together and both pass inspection does the measured thread qualify as acceptable.
- Avoid collisions with hard objects. Handle with care to prevent damage to the measuring surfaces from impacts.
- Never force the thread gauge into threads as a cutting tool to prevent premature wear.
- After use, promptly clean any deposits from the measuring surfaces and store the gauge in the designated gauge case.
Maintenance and Care of Thread Ring Gauges
- Apply rust-preventive oil monthly to ensure surfaces remain free of rust and contaminants (our thread gauges are used frequently in clean environments and do not require oil protection).
- All thread gauges must be calibrated by an accredited metrology calibration agency and remain within their calibration validity period before use.
- Damaged or obsolete thread gauges must be promptly reported for disposal and must not be used further.
- Calibrated thread gauges that exceed measurement tolerances or reach their periodic inspection cycle shall be retrieved by metrology management personnel for appropriate handling.




