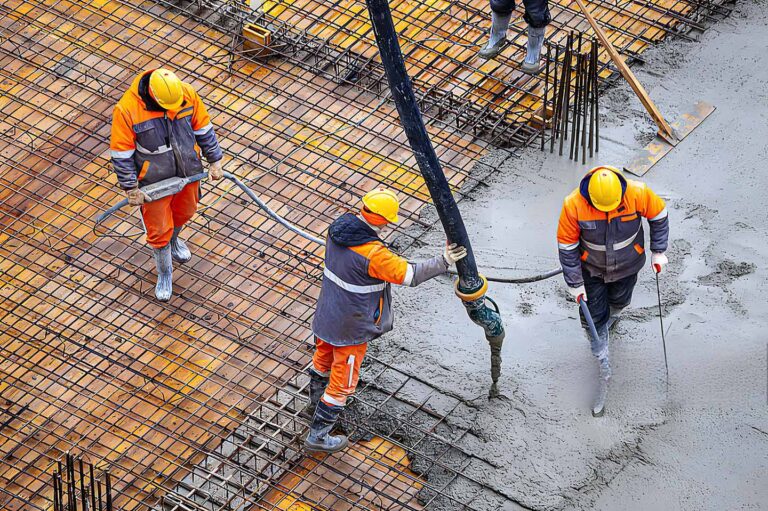
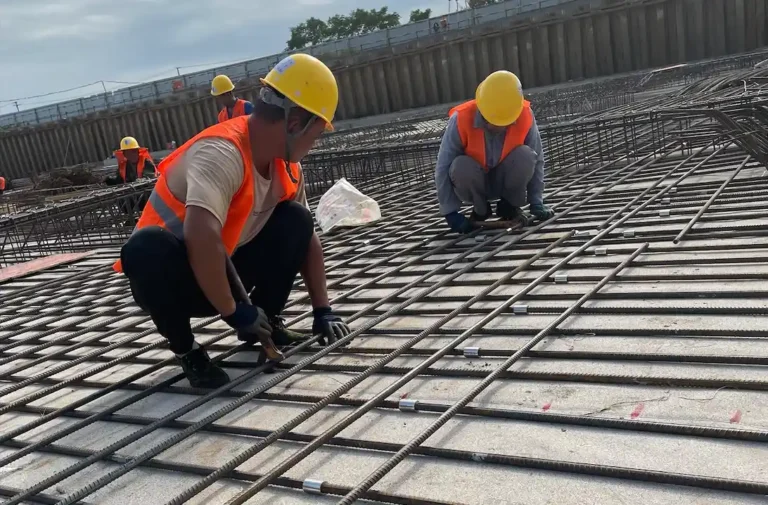
How to install straight threaded rebar sleeve?
Straight threaded rebar sleeve connection, namely: rib-stripping and roll-forming straight threaded sleeve connection, is a mechanical joining method employing cold work hardening. It utilises specialised roll-forming machinery to process the ends of reinforcing bars, inducing plastic deformation to form threads. Two bars are then joined together using a corresponding internal threaded sleeve.
Construction Procedures:
- Reinforcing bar cutting
- Flat-end reinforcement bar cross-section
- Rolled thread processing
- Thread quality inspection
- Cap protection
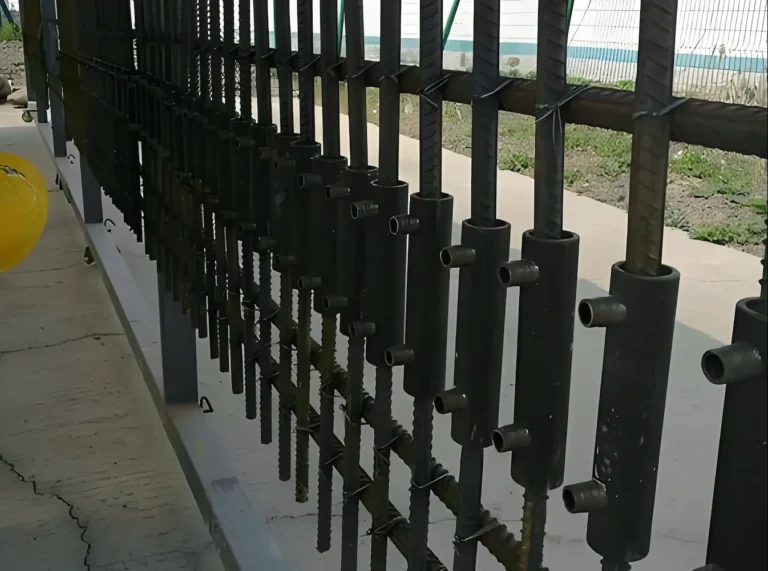
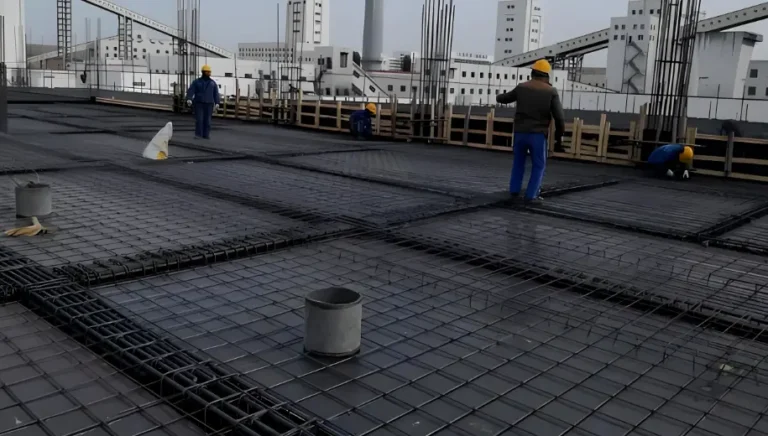
- On-site connection
- Construction inspection
Construction process
- Straight threaded rebar sleeves
- Threaded rebar processing
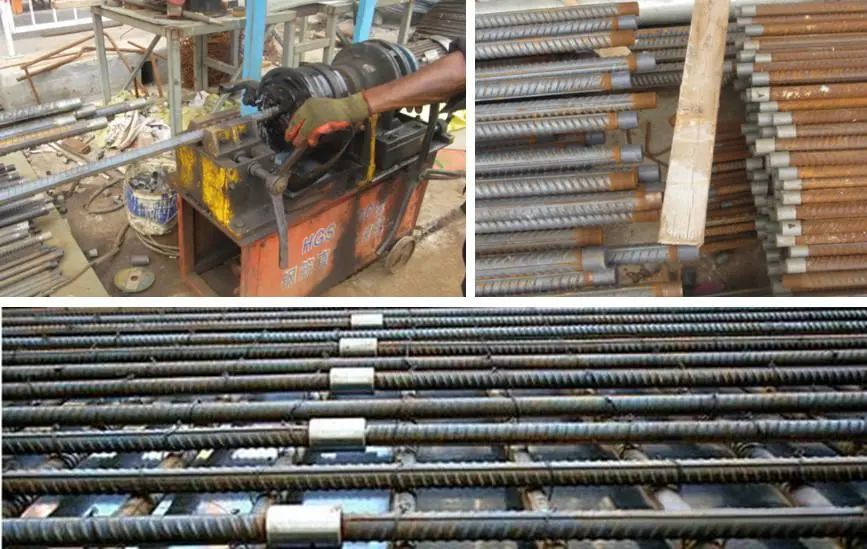

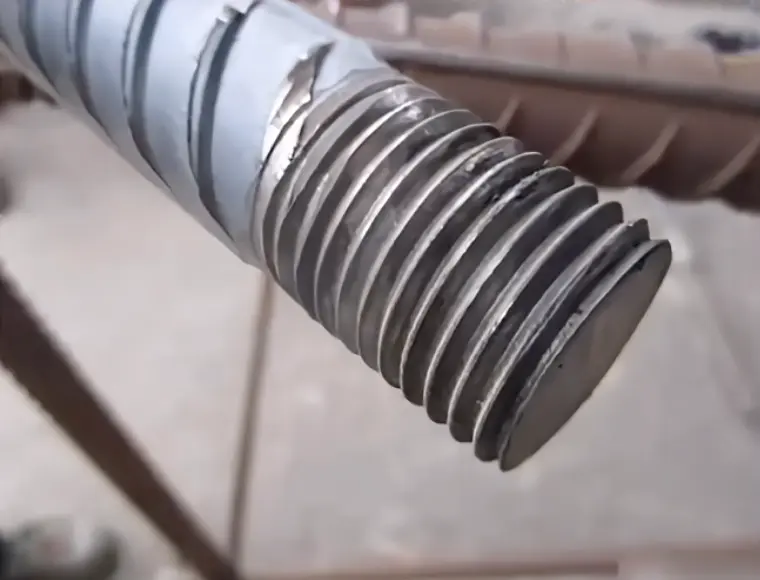
Threaded ends of steel bars processed on site must not exhibit thread misalignment or discontinuous threads.
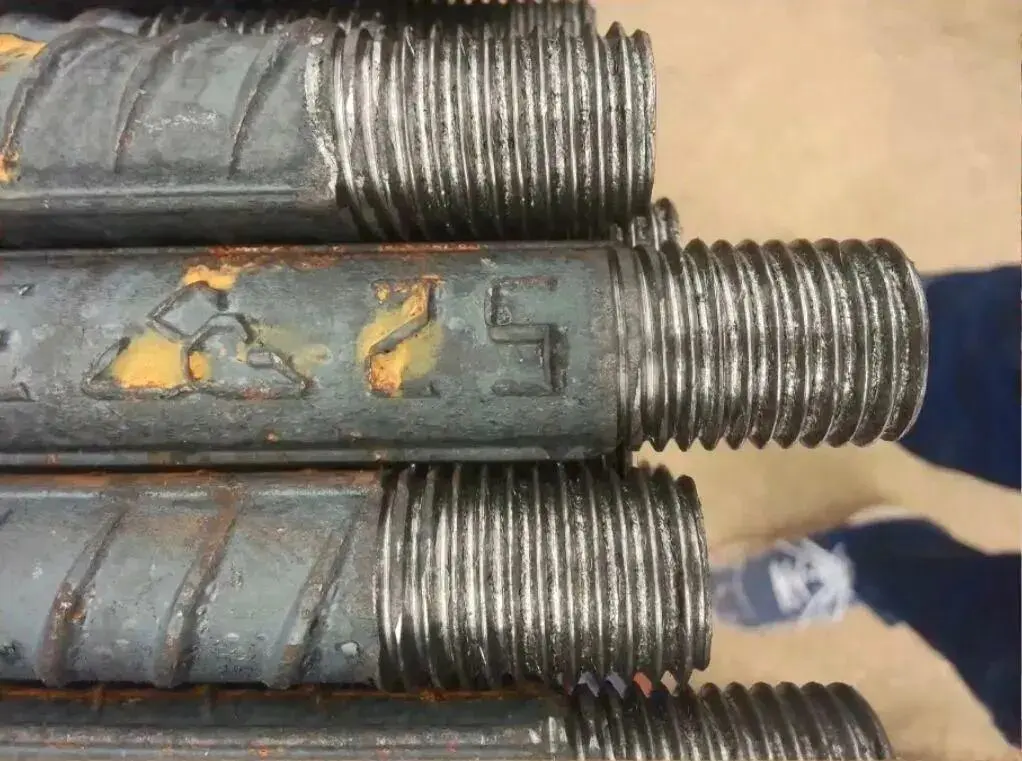

Before threading, use a grinding wheel cutter to grind.
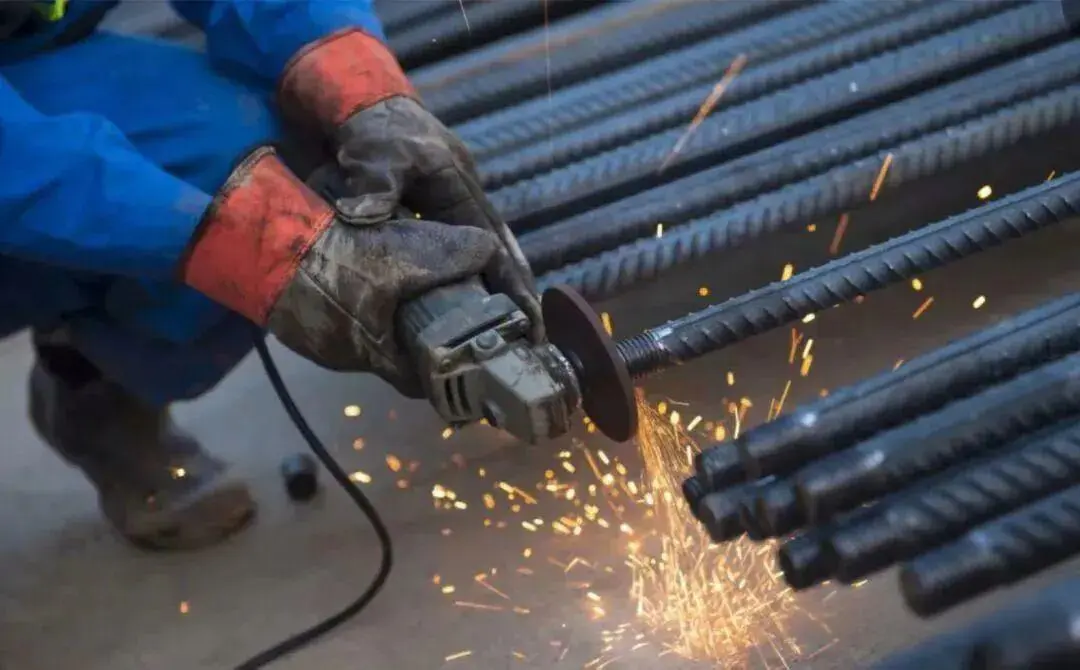

Following threading, inspection shall be conducted using Thread Ring Gauge. The GO gauges shall screw in smoothly and achieve the required insertion length. The No-Go gauge shall not be screwed in beyond 2.5P. A sample of 10% shall be inspected, with the pass rate not falling below 95%.
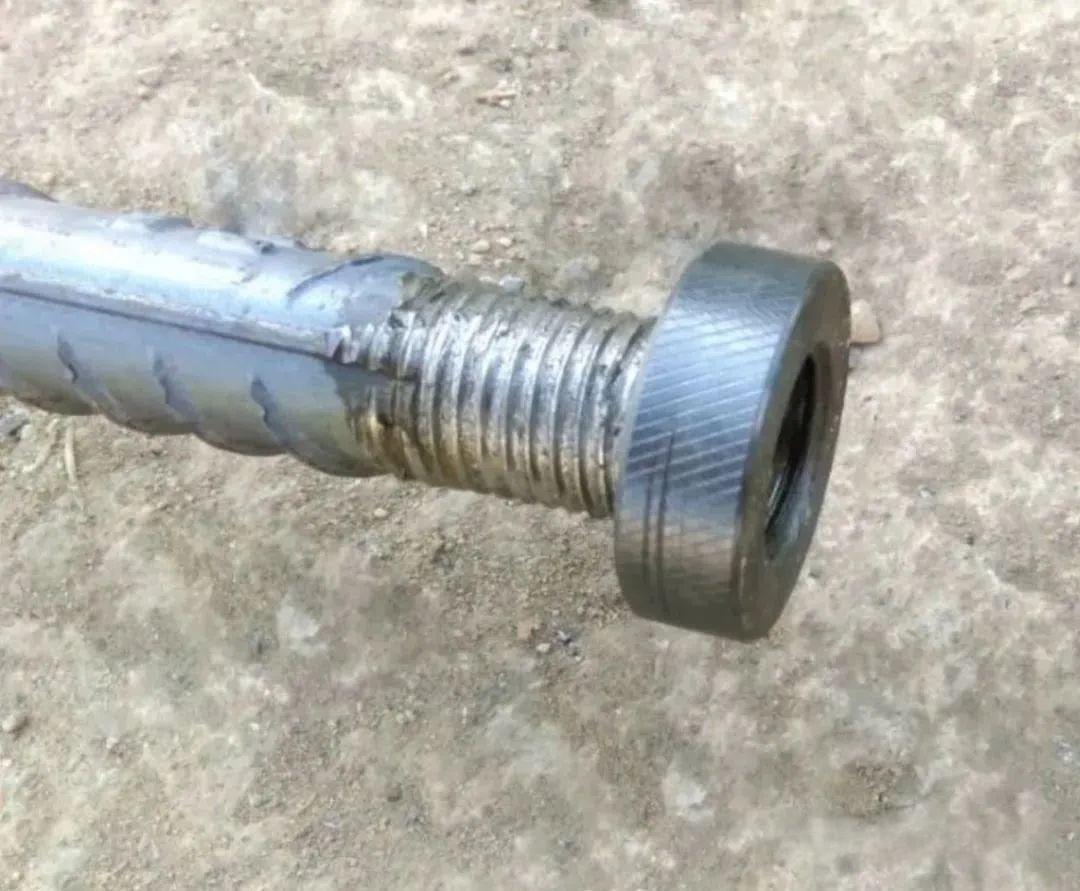
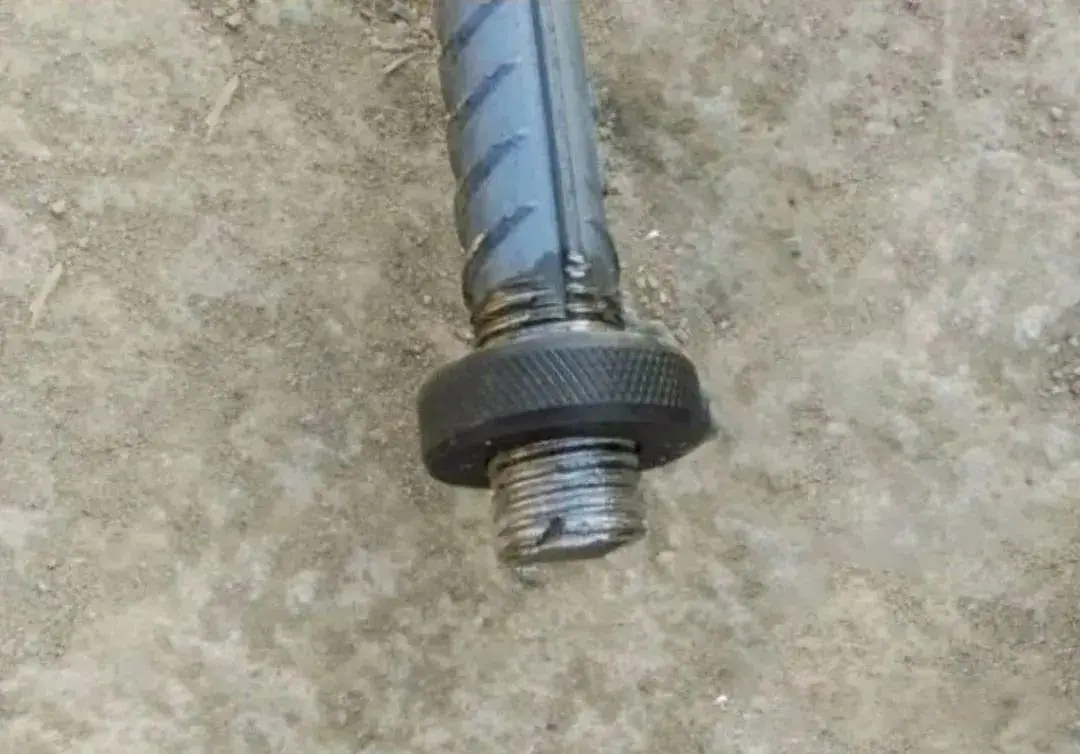
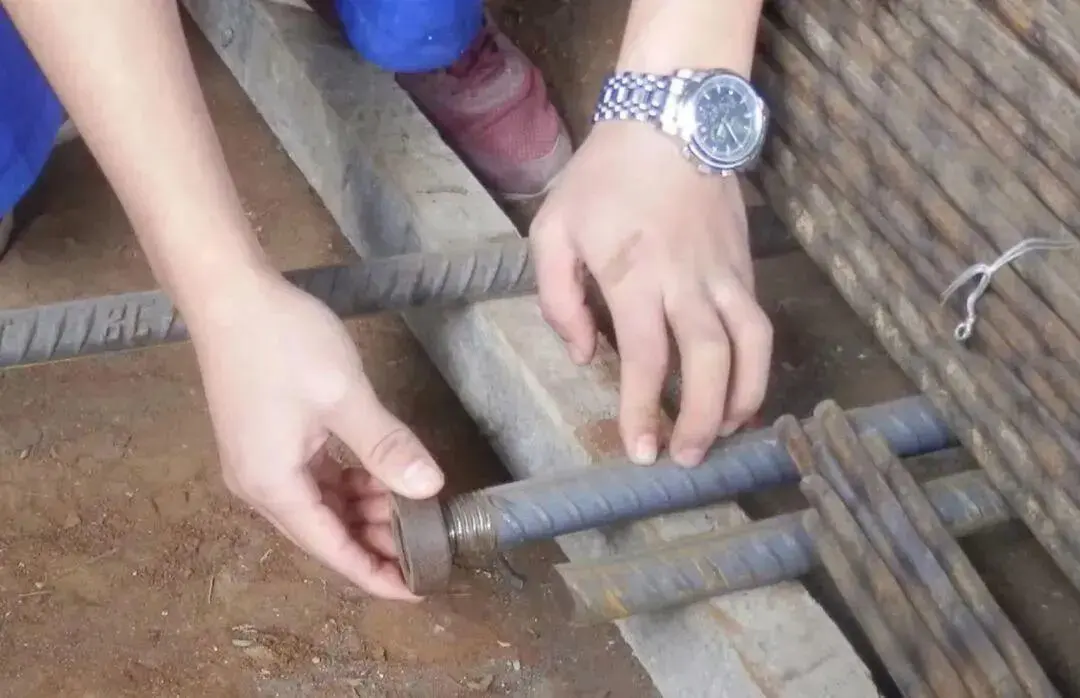
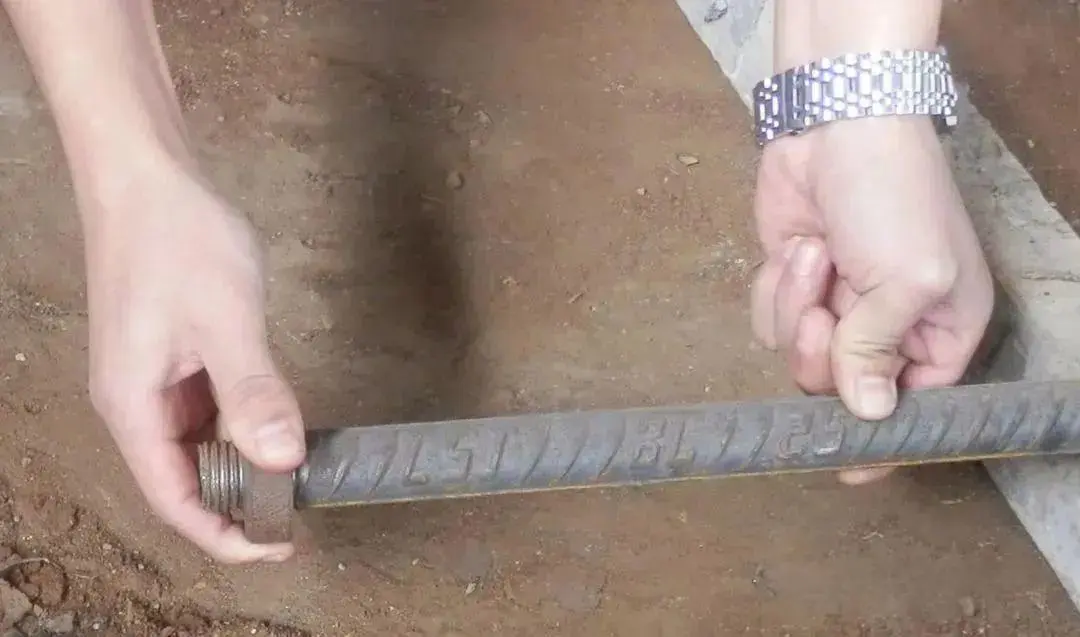





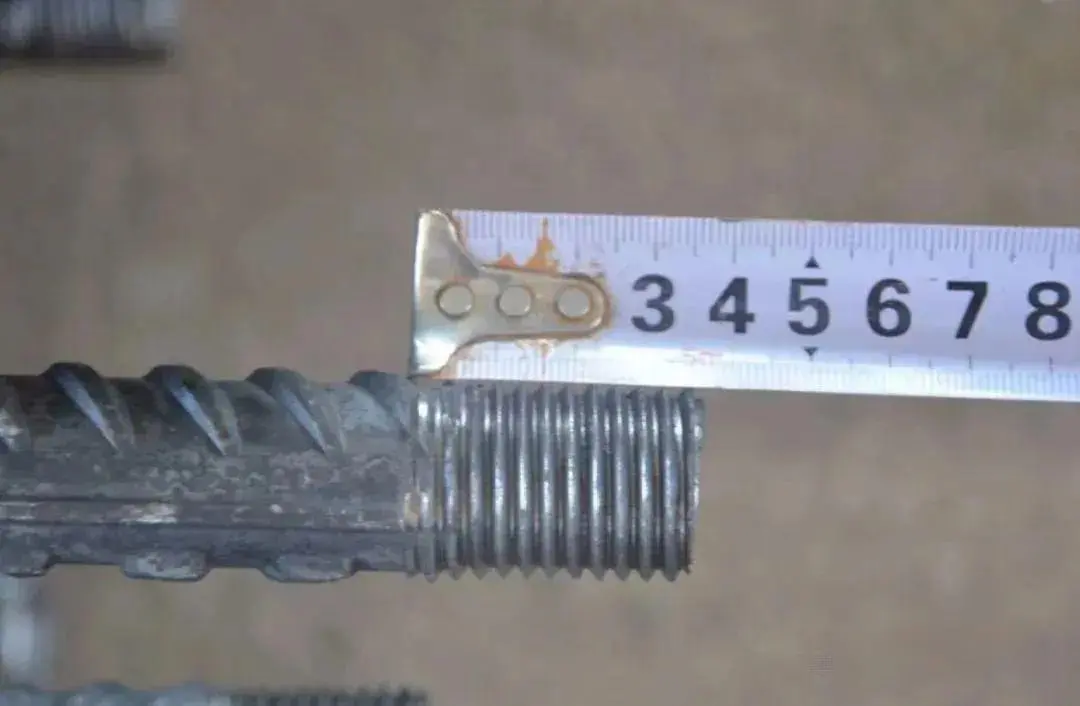
The threaded portion shall be half the length of the sleeve, with a tolerance of 0 to 2P.

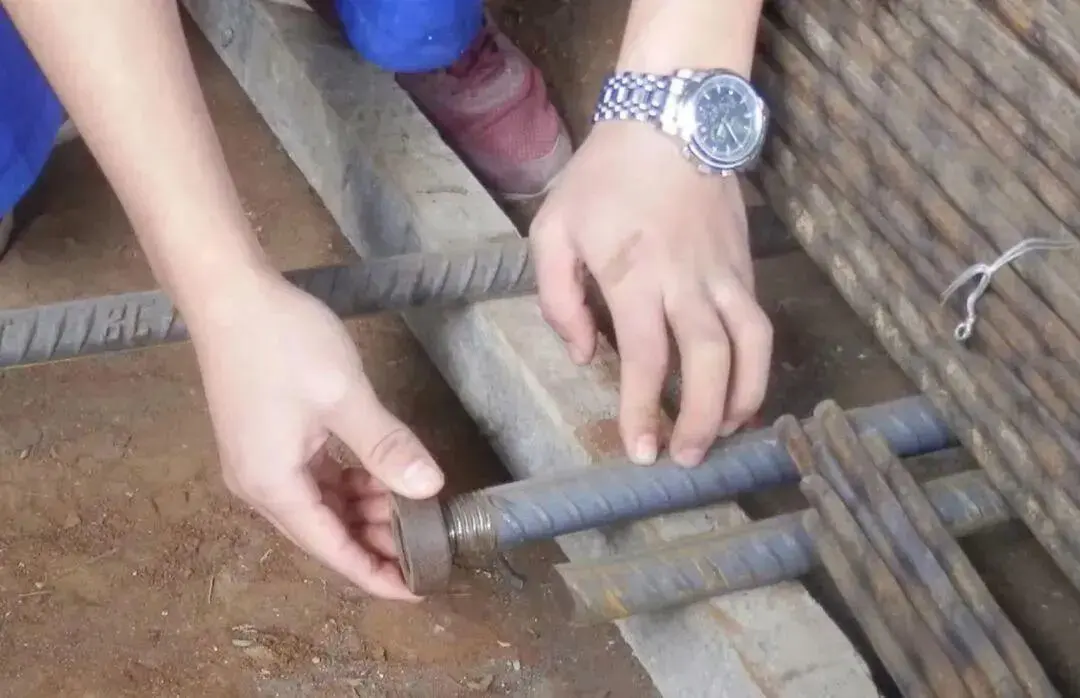
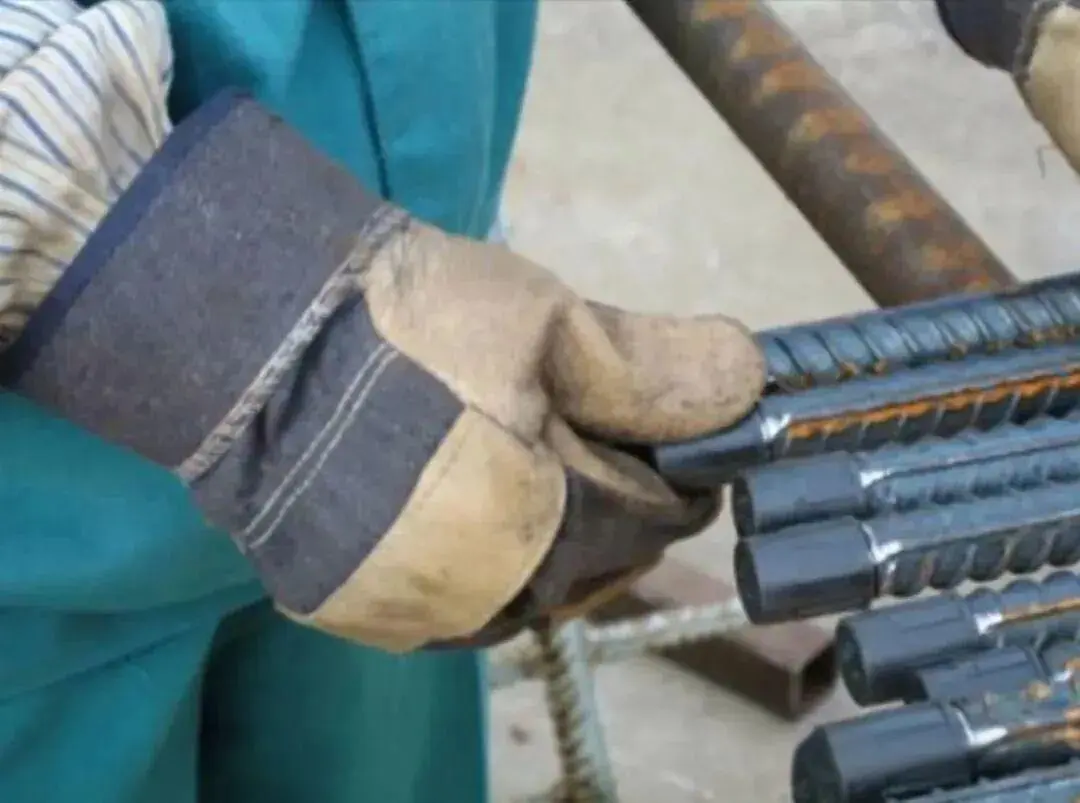
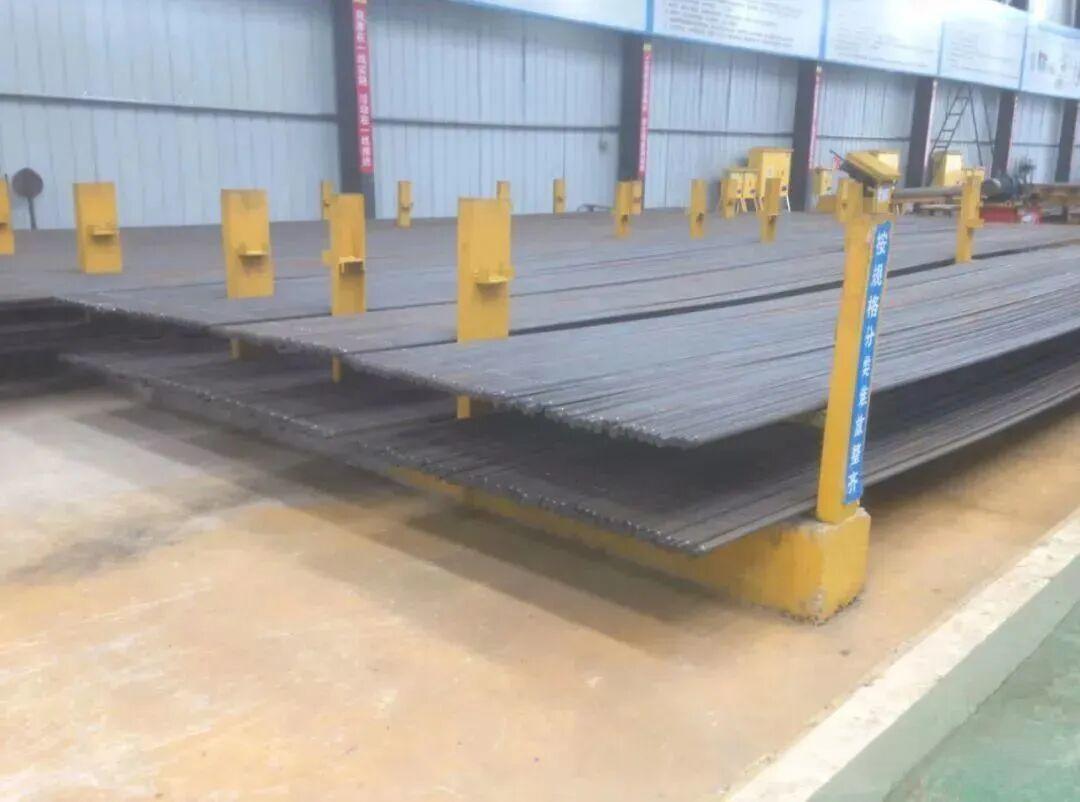
Reinforcing steel threaded ends that have passed inspection shall be protected with thread caps and stacked in a categorised and coded manner.



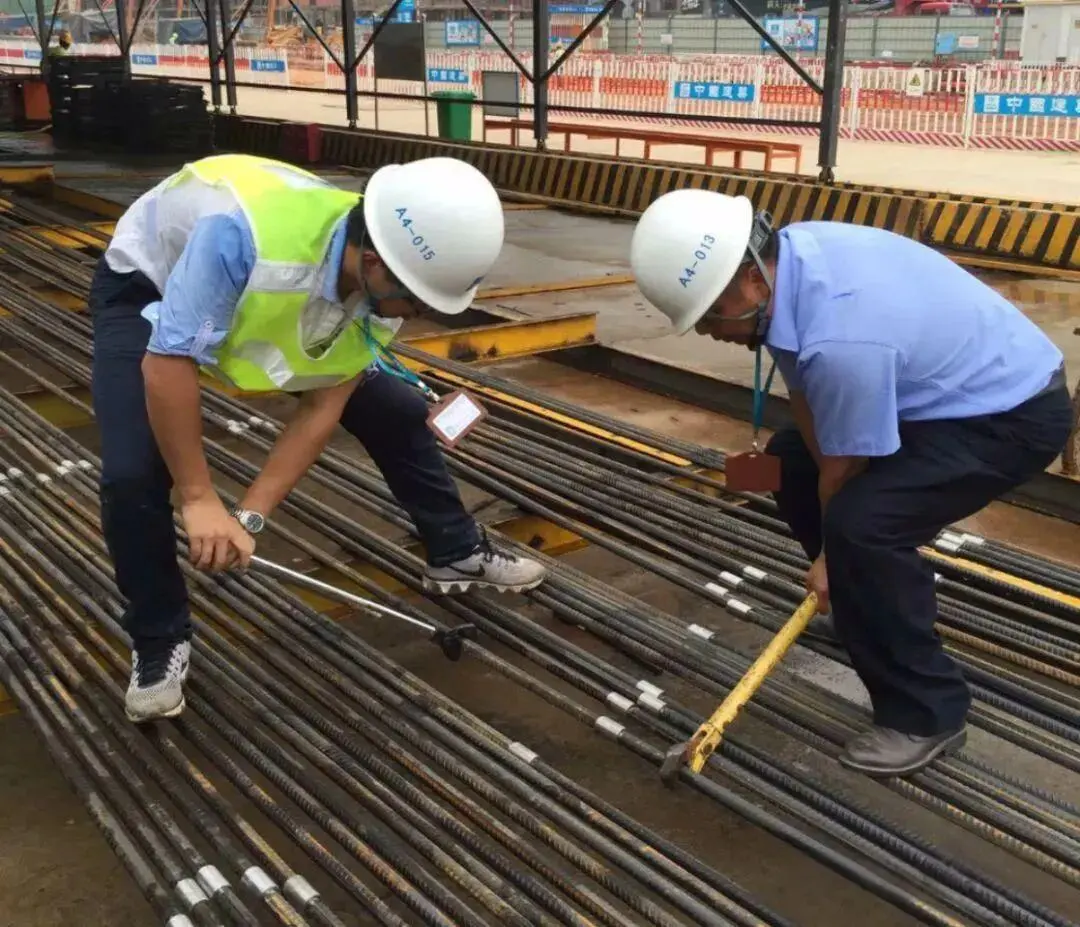
After installing the straight thread sleeves for reinforcing bars, perform torque testing using a torque wrench in accordance with acceptance requirements.
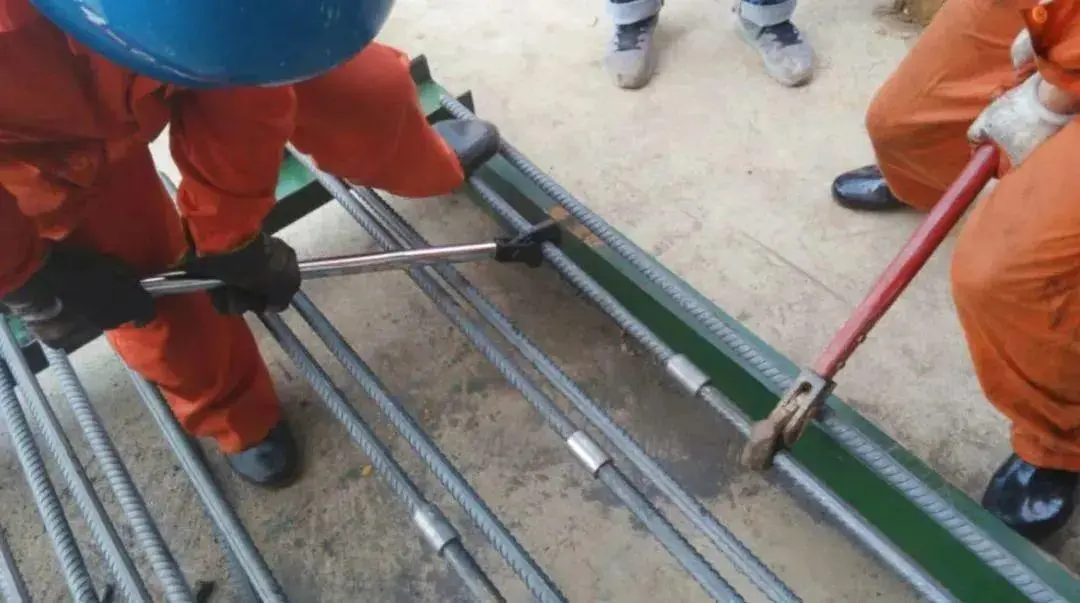


Inspect the supplied rebar coupler
When supplying, it is necessary to provide both the sleeve type inspection report and the sleeve raw material mechanical performance inspection report for the corresponding performance level of the straight threaded steel sleeve. When reviewing the type inspection report, attention should be paid to:
- The test report must detail the fundamental parameters of the joint specimens;
- The test report shall not exceed four years in age;
- Only standard-type joints require a type test report;
- The type test report for HRB500 grade steel bar joints may serve concurrently as the type test report for joints of the same type and grade for HRB400 and HRB335 grades, but the reverse is not permitted.
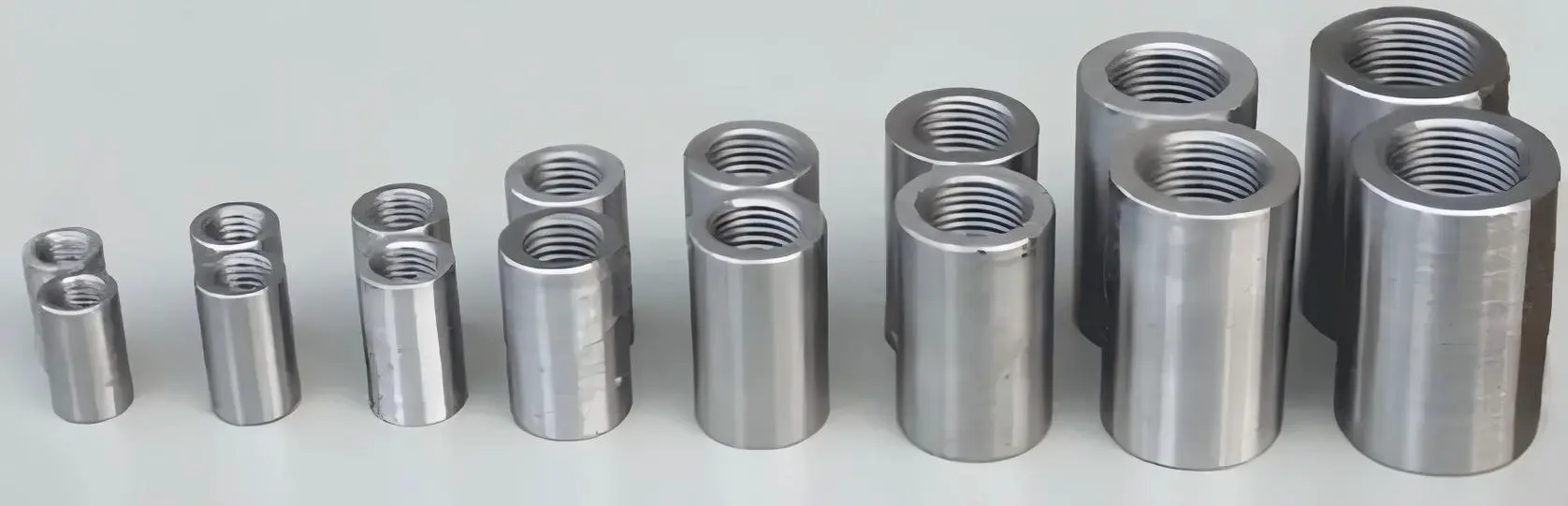
For excavated foundation reinforcement and monolithic hoisting of reinforcement cages, standard straight thread sleeves shall be used for connections. For reinforcement cages requiring segmental hoisting, either reverse thread flared sleeves or locknut sleeves (generally not required) shall be employed.

Visual inspection
The thread profile of the connecting straight threaded rebar sleeve should be full, and there should be no cracks on the surface of the connecting sleeve. The surface and internal threads should not have serious rust or other visible defects.
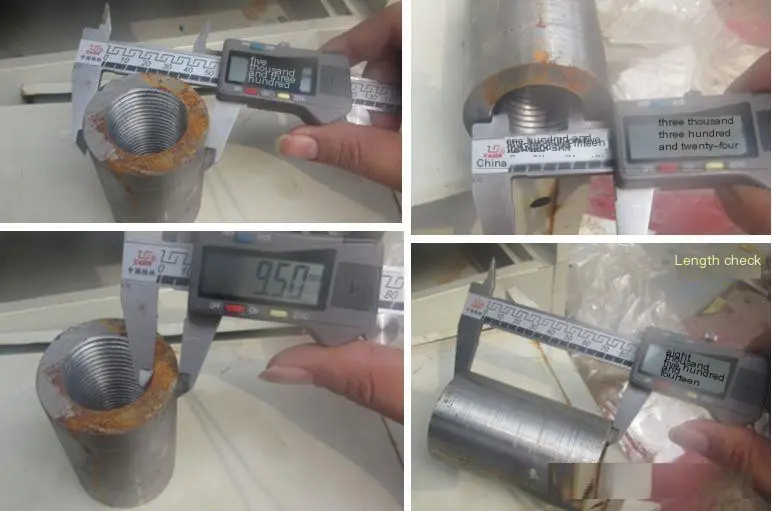
Size inspection
Critical dimensions (outer diameter, length), thread profiles, and precision shall be verified to meet the manufacturer’s product design drawings. Internal threads shall be inspected using dedicated thread plug gauges. The pass plug gauge shall screw in smoothly, while the stop plug gauge shall not be screwed in beyond 3P (where P is one pitch length).

Allowable deviation: sleeve diameter D ≤ 50; Allowable deviation of outer diameter ± 0.5; The allowable deviation for length is ± 0.5.

Sample collection and submission for testing
General Test Items: Tensile Strength.
Acceptance Batch and Sampling Quantity
Joints of the same grade and specification from the same batch of materials under identical construction conditions shall be grouped into acceptance batches of 500 units for inspection and acceptance. Batches with fewer than 500 units shall also be treated as a single acceptance batch. Three specimens shall be randomly selected from each acceptance batch for uniaxial tensile testing. The tensile test specimens shall be 600 mm long, with the joint located at the midpoint of the specimen.

The sampling form shall include the following information: commissioning entity, project name, construction unit, sampling date, rebar manufacturer or origin, rebar grade or designation, rebar specifications, welding connection method, application location, number of test specimen sets, required inspection items, sampler, witness, and witness number.
Qualification Rate Requirements:
The qualification rate for random inspections of connecting sleeves or lock nuts shall not be less than 95%. When the qualification rate of a random inspection falls below 95%, an additional sample of the same quantity shall be drawn for re-inspection. The batch shall be deemed qualified if the combined qualification rate of both inspections is not less than 95%. If the qualification rate remains below 95%, each item in the batch shall undergo individual inspection. Only qualified items may be used, while non-conforming items shall be returned to the manufacturer for handling.
Other Notes
- Threading operations must be performed by trained, certified personnel. Operators for the same machine shall not be arbitrarily changed. Before commencing work, the worker must first produce a threaded end that passes inspection to avoid losses from indiscriminate mass production.
- Threaded ends must be cut flush at both ends of the rebar (using a grinding wheel cutter; gas cutting is strictly prohibited). Ensuring flat ends allows installation torque to effectively counteract each other, thereby eliminating or reducing deformation caused by thread gaps when the rebar is under tension.

- The processing length of rebar threads should generally be two full thread turns longer than the socket length (equivalent to half the socket length).

- After threading, test the connection by tightening it with a sleeve to ensure quality. Apply protective caps immediately (as exposed rebar rusts easily after oxide layer removal).
- During the rebar tying phase, frequent on-site inspections are required to monitor usage (preventing waste), verify correct application methods, and assess whether mechanical connections achieve required torque strength (e.g., using a torque wrench to apply force downward with body weight to test resistance).
- Before formwork closure and concrete pouring, conduct on-site checks to ensure materials are cleared away, avoiding unnecessary waste.






